





Motion Sensing
How does motion sensing work?
There are many different ways to create a motion sensor.
Some examples include:
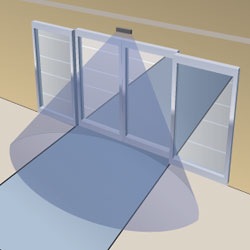
* Many grocery stores have automatic door openers that use a very simple form of radar to detect when someone passes near the door. The box above the door sends out a burst of microwave radio energy and waits for the reflected energy to bounce back. When a person moves into the field of microwave energy, it changes the amount of reflected energy or the time it takes for the reflection to arrive, and the box opens the door. Since these devices use radar, they often set off radar detectors.
* It is common for stores to have a beam of light crossing the room near the door, and a photosensor on the other side of the room. When a customer breaks the beam, the photosensor detects the change in the amount of light and rings a bell.
* The same thing can be done with ultrasonic sound waves, bouncing them off a target and waiting for the echo.
All of these are examples of active sensors. They inject some form of energy (light, microwaves or sound) into the environment in order to detect some sort of change.
A common application of motion sensing technology can be seen outside many private homes. Many houses have motion sensing lights installed outside to save energy and deter burglary. You have probably noticed that these types of lights are sensitive to motion, but not to a person who is standing still. This result is due to the fact that the electronics package attached to the sensor is looking for a fairly rapid change in the amount of infrared energy it is seeing. Thus, when a person walks past a motion sensing light, the amount of infrared energy in the field of view changes rapidly and is easily detected. You do not want the sensor detecting slower changes in infrared energy, like a sidewalk cooling during the night.

Bluetooth

The WiiMote transmits signals to the computer via a Bluetooth connection. Due to innovation by people at the WiiLinux project, anyone with a Bluetooth receiver in their computer has the ability to create this connection. Through the use of certain programs as mapping agents, WIIMote buttons and accelerometer axes to perform the action of any keyboard button or mouse movement.

The Nintendo Wii


When many gamers think of the Motion Sensor (aka Tilt Cartridge) in video games, they think of the Game Boy Advance game Wario Ware: Twisted was the first Game Boy title to use Motion Sensors. However, they would be wrong. The use of motion sensing in games started with a little GBC game called Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble. The motion sensor, aka tilt cartridge, used in this game senses how you move the GBC and how short and fast you shift it. This feature allows you to use the system as a controller. In Kirby Tilt 'n' Trouble, how you tilt the GBC controls Kirby - you can even make him jump through a quick jerk of the wrists.
Gyration: The Company Behind the WiiMote
Starting in California in 1989, Gyration's goal was to develop the use of gyroscope technology for computer and television interfaces. They made significant contributions in the field of gyroscope technology throughout the 1990's. In 2001, Gyration created the first motion sensing Nintendo controller prototype. It was this prototype that would eventually lead to the production of the WiiMote. The WiiMote uses Gyrations technology of a tiny gyroscope and a 3-axis accelerometer to precisely track the movement of the WiiMote.
Accelerometers are used to measure the specific external forces acting upon a device or object. Specific external force is calculated by adding the sum of the external forces upon the object, then dividing that by the mass of the object. With this data, the accelerometers allow the device the calculate its own position and utilize this data for another action, such as moving a cursor on a screen.



