Resistive Touch Screens
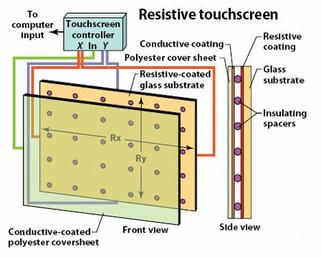
Composition: The resistive touch screen is a glass panel covered with a conductive and resistive metallic layer. The two layers are held apart by spacers and there is a scratch resistant layer placed on the top of the glass. Electrical current runs through the two layers when the monitor is operational, when it it touched the two layers make contact and the coordinates are recorded. (conductive layers are typically indium tin oxide for increased clarity)
Benefits:
Problems:
More information:
Benefits:
- Reliable and durable
- Most contamination resistant available
- drift-free operation - lasts over 35 million finger touches
- scratch resistant and withstands heavy-usage environments
- coversheet stays tight with environmental changes
Problems:
- lacks clarity compared to other screens
- easily damaged by sharp objects
More information:
- most common touch screen in use today
- Multi-touch capabilities
- Touch is based on the amount of pressure used
- Used in point-of-scale, industrial, and medical applications
- flat panel and CRT solutions are available
- Can be used with a finger, a gloved hand, a fingernail, or objects such as a credit card including a stylus
- 4-wire and 5-wire are the different types of touch screens - Accutouch is a 5-wire resistive screen made by Elographics
- Examples: LG Optimus, LG, Vu, LG GW620, Sony Ericsson Vivaz, Nokia N97 mini, and the Nokia N900 - all of these are examples of phones in the market today
Capacitive Touch Screens
Composition: It is made of an indium tin oxide sheet that stores an electrical charge that is on the glass of the display. When the glass is touched a small quantity of the charge is transmitted to the users finger and the quantity of charge on the screen reduces. The reduction is calculated in the circuits situated at the corner of the display. The processor computes where the display was touched from comparative variation in the charge at every corner.
Benefits:
Problems:
More Information:
Benefits:
- more clarity than resistive
- more user friendly - great dragging capabilities
- scratch and abrasion resistant
- the touch performance isn't affected by the external environment
- quick response
- operates drift-free in areas of poor grounding
Problems:
- more expensive than resistive
- can only be touched with a bare finger
More Information:
- multi-touch capabilities
- Capacitive touch capabilities have been expanded to projections. The display is projected to a suspended piece of glass or to windows.
- Examples: iPhone, iPad, HTC Desire, Samsung Galaxy S, and Samsung Wave
Surface - Wave Touch Screens
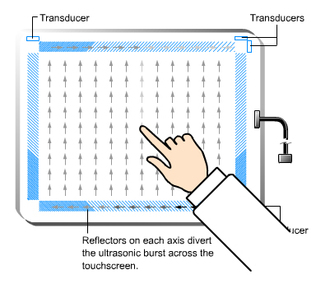
Composition: The screen is made up of two transducers (1 sending and 1 receiving) placed along the X and Y axes of the monitor's glass plate. Reflectors on the glass reflect an electrical signal sent from one transducer to the other. The receiving transducer recognizes wave disruption by touch and locates it accordingly. (Ultrasonic waves are used in this type of screen)
Benefits:
Problems:
More Information:
Benefits:
- Stable drift-free operations
- quick response
- superior clarity due to no metallic layers
- physically impossible to wear out
- can come with tempered glass construction that has superior resistance to breakage and vandalism
Problems:
- easily damaged by outside elements (dust and water)
- most expensive touch screen
More Information:
- recognizes the amount of pressure applied to the screen
- can be used with a finger, a gloved hand, or a soft stylus
- Used in kiosks, gaming, and office automation applications
- Available in flat panel and CRT solutions
- multi-touch capabilities
- IntelliTouch is the surface-wave touch screen created by Elographics
Infrared Touch Screens
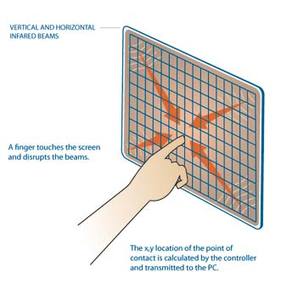
Composition: There are two types of infrared touch screens. One kind is a screen that is set up to react to infrared or thermal waves, however, this screen is slow and doesn't work well with cold hands, objects or the environment.
The second type of infrared touch screen is made up of vertical and horizontal infrared sensors around the perimeter of the screen. These sensors create a grid that pinpoints the location of the touch and sends the location to the computer.
Benefits:
Problems:
More Information:
The second type of infrared touch screen is made up of vertical and horizontal infrared sensors around the perimeter of the screen. These sensors create a grid that pinpoints the location of the touch and sends the location to the computer.
Benefits:
- This type of screen is very durable.
Problems:
- this screen typically has slower response times
- This type of screen can't be used with anything but a warm hand since it senses the heat of the user's finger.
More Information:
- This type of screen is typically used in industrial and military applications.
- Examples of phones in the market that used infrared are the Samsung U600 and the Samsung SGH E900.